June 1st is Heimlich Maneuver Day. You may think you know everything you need to know about this procedure and the man who may or may not have invented it. But, stick around because this one gets weird.
In 1974, the journal Emergency Medicine published Dr. Henry Heimlich’s article about a method to combat choking that has saved countless lives.

At the time, a series of blows to the back was the treatment of choice. Thoracic surgeon Heimlich said he set out to find a better way and realized that when choking, air is trapped in the lungs. When the diaphragm is elevated, the air is compressed and forced out along with the obstruction.
He anesthetized a beagle to the verge of unconsciousness, plugged its throat with a tube, then conducted experiments to find an easy way to get the dog to expel it. After succeeding, he reproduced the result with three other beagles.
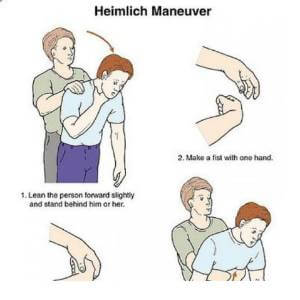
Refined for use on humans, his technique entails standing behind the choking person, making a fist below the sternum but above the belly button, and pulling it in and up to dislodge the blockage.
In 1976, the Heimlich maneuver became a secondary procedure to be used only if back blows were unsuccessful. In 1986, the American Heart Association (AHA) revised its guidelines, recommending the Heimlich maneuver as the primary option for rescuers.
Heimlich was a fierce proponent of using the procedure to rescue drowning victims, but the AHA warns it can lead to vomiting, aspiration pneumonia, and death.
But his most controversial theory is “malariotherapy,” the practice of infecting a patient with malaria to treat another ailment. Although he had no expertise in oncology, Heimlich was convinced it could treat cancer.
In 1987, after the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) refused to supply him with infected blood, he went to Mexico City and convinced the Mexican National Cancer Institute (MNCI) to allow him to treat five patients with malariotherapy. Four of the patients died within a year. The project was abandoned with no follow-up studies.
In 1990, The New England Journal of Medicine published Heimlich’s letter proposing malariotherapy as a treatment for Lyme disease. Before long, sufferers around the world began to ask for the treatment. But lack of supporting evidence and poor patient reviews spelled the end of the exercise.
Within a few years, he decided it could tackle AIDS. Anthony Fauci, Director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), labeled the idea “quite dangerous and scientifically unsound.” However, Heimlich was able to secure financing from Hollywood donors and establish a clinic in China.
In 1994, his Heimlich Institute paid four Chinese doctors between $5,000 and $10,000 per patient to inject at least eight HIV patients with malarial blood. At the 1996 International Conference on AIDS, he announced that in two Chinese patients, CD4 counts that decrease as HIV progresses to AIDS, had increased after malariotherapy and remained elevated two years later.
When experts reviewed the studies, they found that the test used by Chinese doctors to measure CD4 levels was notoriously unreliable, rendering the results useless. Heimlich pressed on, but this time had a difficult time finding sponsors.
In 2005, Heimlich determined that a rebranding was in order. Reasoning that the word “malaria” might scare people off, he changed the name to “immunotherapy.” When speaking to a journalist, he refused to disclose the exact location of his latest clinical trial in Africa. Due to its ethically dubious practice of initially denying treatment for malaria, the study had been conducted without governmental permission.
That same year, the AHA undertook a de-branding effort: its guidelines no longer refer to the Heimlich maneuver by name. It is now simply referred to as an “abdominal thrust.” Since 2002, Heimlich’s son Peter has worked to pierce the myth surrounding his father, labeling him a fraud and exposing alleged human rights abuses, including experimentation on unwitting people in violation of international ethical standards regarding informed consent.
On Monday, May 23, 2016, the 96-year-old reportedly performed his maneuver on 80-year-old Patty Ris, a fellow resident at Deupree House, a senior living community in Cincinnati, Ohio. He told a reporter it was the first time he’d used his invention to save a life. (In 2003, he told BBC Online News that he’d saved someone at a restaurant three years earlier.) While many news outlets reported it as fact, some came to question its veracity.
While it’s an understatement to say that Dr. Henry Heimlich was a complex and problematic individual, there is no denying that he created a life-saving procedure. Unless he didn’t. According to emergency room physician Edward Patrick, he helped develop the maneuver before Heimlich took sole credit and slapped his name on it.
Patrick’s backstory is bizarre, including a possible scam involving “saving” a girl from drowning to help Heimlich convince the AHA to recommend it. (As mentioned earlier in the post, AHA rejected it. And in reality, the girl slipped into a coma and died four months later.) We’re not saying any of this is true, of course. Along with every other allegation, Patrick is allegedly quite litigious.
However you decide to celebrate it, have a happy day free of the need for the Heimlich maneuver!
 Today is Festival of Popular Delusions Day. It is said to have originated in Germany on June 5th, 1945. Let’s begin with some background information about this mysterious holiday.
Today is Festival of Popular Delusions Day. It is said to have originated in Germany on June 5th, 1945. Let’s begin with some background information about this mysterious holiday.



